路径操作
pathlib 是跨平台的、面向对象的路径操作模块,可适用于不同的操作系统,其操作对象是各种操作系统中使用的路径(包括绝对路径和相对路径)。
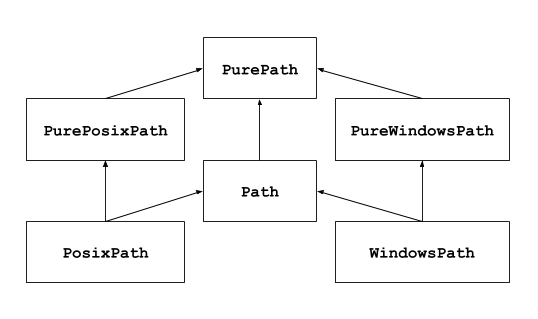
pathlib 与 os 的区别
在 Python 3.4 之前,涉及路径相关操作,都用 os 模块解决,尤其是 os.path 这个子模块非常有用。在 Python 3.4 之后,pathlib 成为标准库模块,其使用面向对象的编程方式来表示文件系统路径,丰富了路径处理的方法。
pathlib 优势
相对于 os 模块,pathlib 模块具体如下优势:
- 实现统一管理,解决了传统操作导入模块不统一问题;
- 使得在不同操作系统之间切换非常简单;
- 是面向对象的,路径处理更灵活方便,解决了传统路径和字符串并不等价的问题;
- 简化了很多操作,简单易用。
pathlib 和 os 操作对比
通过常用路径操作的对比,可以更深刻理解 pathlib 和 os 的区别,便于在实际操作中做对照,也便于进行使用替代,详细对比如下:
| pathlib 操作 | os 操作者 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Path.resolve() | os.path.abspath() | 获得绝对路径 |
| Path.chmod() | os.chmod() | 修改文件权限和时间戳 |
| Path.mkdir() | os.mkdir() | 创建目录 |
| Path.rename() | os.rename() | 文件或文件夹重命名,如果路径不同,会移动并重新命名 |
| Path.replace() | os.replace() | 文件或文件夹重命名,如果路径不同,会移动并重新命名,如果存在,则破坏现有目标。 |
| Path.rmdir() | os.rmdir() | 删除目录 |
| Path.unlink() | os.remove() | 删除一个文件 |
| Path.unlink() | os.unlink() | 删除一个文件 |
| Path.cwd() | os.getcwd() | 获得当前工作目录 |
| Path.exists() | os.path.exists() | 判断是否存在文件或目录 name |
| Path.home() | os.path.expanduser() | 返回电脑的用户目录 |
| Path.is_dir() | os.path.isdir() | 检验给出的路径是一个文件 |
| Path.is_file() | os.path.isfile() | 检验给出的路径是一个目录 |
| Path.is_symlink() | os.path.islink() | 检验给出的路径是一个符号链接 |
| Path.stat() | os.stat() | 获得文件属性 |
| PurePath.is_absolute() | os.path.isabs() | 判断是否为绝对路径 |
| PurePath.joinpath() | os.path.join() | 连接目录与文件名或目录 |
| PurePath.name | os.path.basename() | 返回文件名 |
| PurePath.parent | os.path.dirname() | 返回文件路径 |
| Path.samefile() | os.path.samefile() | 判断两个路径是否相同 |
| PurePath.suffix | os.path.splitext() | 分离文件名和扩展名 |
常用方法
获取目录
- Path.cwd(),返回文件当前所在目录;
- Path.home(),返回电脑用户的目录。
python
>>> from pathlib import Path
>>> print(Path.cwd())
D:\zhengxin_docs
>>> print(Path.home())
C:\Users\zhengxinonly目录拼接
拼接出 Windows 桌面路径,当前路径下的子目录或文件路径。
python
>>> Path(Path.home(), "Desktop")
WindowsPath('C:/Users/zhengxinonly/Desktop')
>>> Path.joinpath(Path.home(), "Desktop")
WindowsPath('C:/Users/zhengxinonly/Desktop')
>>> Path.cwd() / 'test'
WindowsPath('D:/zhengxin_docs/test')路径处理
获取路径的不同部分、或不同字段等内容,用于后续的路径处理,如拼接路径、修改文件名、更改文件后缀等。
python
>>> input_path = r"C:\Users\zhengxinonly\Desktop\test.py"
>>> Path(input_path).name # 返回文件名 + 文件后缀
'test.py'
>>> Path(input_path).stem # 返回文件名
'test'
>>> Path(input_path).suffix # 返回文件后缀
'.py'
>>> Path(input_path).suffixes # 返回文件后缀列表
['.py']
>>> Path(input_path).root # 返回根目录
'\\'
>>> Path(input_path).parts # 返回文件
('C:\\', 'Users', 'zhengxinonly', 'Desktop', 'test.py')
>>> Path(input_path).anchor # 返回根目录
'C:\\'
>>> Path(input_path).parent # 返回父级目录
WindowsPath('C:/Users/zhengxinonly/Desktop')
>>> Path(input_path).parents # 返回所有上级目录的列表
<WindowsPath.parents>路径判断
- Path.exists(),判断 Path 路径是否是一个已存在的文件或文件夹;
- Path.is_dir(),判断 Path 是否是一个文件夹;
- Path.is_file(),判断 Path 是否是一个文件。
python
>>> input_path = r"C:\Users\zhengxinonly\Desktop\test.py"
>>> Path(input_path).exists()
True
>>> Path(input_path).is_file()
True
>>> Path(input_path ).is_dir()
False