Button 组件
Button 组件是用于实现一个按钮,它的绝大多数选项跟 Label 组件是一样的。不过 Button 组有一个 Label 组件实现不了的功能,那就是可以接收用户的信息。Button 组件有一个 command 选项,用于指定一个函数或方法,当用户单击按钮的时候,tkinter 就会自动地去调用这个函数或方法了。
Button 是一个标准的 tkinter 的控件,用于实现各种按钮。按钮可以包含文本或图像,当 Button 的点击事件绑定某个函数 (方法) 时,按下 Button 会自动调用该函数或方法。
基本用法与可选属性
基本用法
基本用法:Button(根对象, [属性列表])
根对象:在那个窗体显示,例如主窗体。
属性列表:是可选的属性=属性值组成。
可选属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| text | 标签显示的文本 |
| font | 设置文本的字体和大小 |
| fg(foreground) | 字体的颜色, |
| bg (background) | 标签的背景色 |
| width | 标签的宽度(一个中文的字体宽为单位) |
| height | 标签的高度(一个中文的字体高为单位) |
| cursor | 鼠标的样式 |
| command | 绑定事件 |
| padx | 文字到边框的距离,水平方向 |
| pady | 文字到边框的距离,垂直方向 |
| bd(borderwidth) | 边框的宽度 |
| relief | 边框的样式 |
| justify | 文本对齐方式 |
| image | 图片 |
| compound | 图片与文字的混搭 |
| anchor | 方位 |
可选属性的具体应用
常用属性
常用属性 text, font, foreground, background, width, height 使用方式与 Label 组件完全一致使用方式可以参考上文,不重复赘述。
代码:
python
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("500x300+100+100")
# 普通按钮
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="Button1")
button1.pack()
# 背景与前景色
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="Button2", bg="#00ffff", fg="red")
button2.pack()
# 宽度与高度
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="Button3", width=10, height=2)
button3.pack()
# 边距
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="Button4", padx=10, pady=10)
button4.pack()
root.mainloop()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
效果演示:
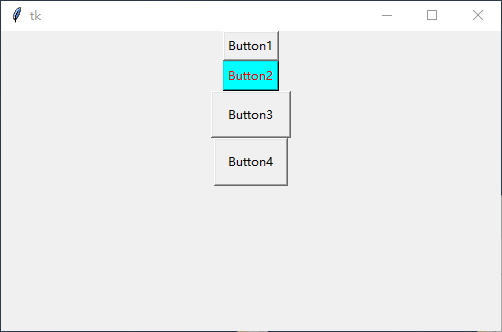
图片按钮
使用方式、特性与 Label 一致
python
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("500x300+100+100")
img2 = tk.PhotoImage(file="../../assets/logo.png")
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="Button1", image=img2)
button1.pack()
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="Button2", image=img2, compound="left")
button2.pack()
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="Button3", image=img2, compound="right")
button3.pack()
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="Button4", foreground="red", image=img2, compound="center")
button4.pack()
root.mainloop()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
演示效果:
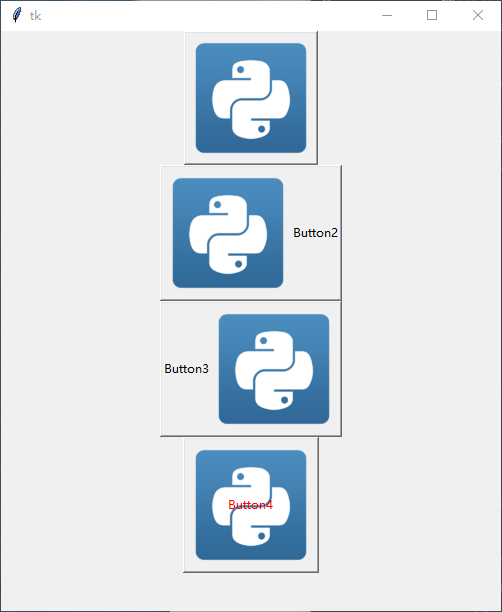
边距与对齐方式
边距:padx,pady 与文本对齐方式:justify 使用方式与 Label 一致
代码:
python
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
# 边距
button1 = tk.Button(root, text='padx pady 默认')
button1.pack()
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="padx=0, pady=0", padx=0, pady=0)
button2.pack()
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="padx=10, pady=10", padx=10, pady=10)
button3.pack()
# 对齐方式
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="学 python 找正心\n有福利哦")
button4.pack()
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="学 python 找正心\n有福利哦", justify="left")
button4.pack()
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="学 python 找正心\n有福利哦", justify="right")
button4.pack()
root.mainloop()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
演示效果
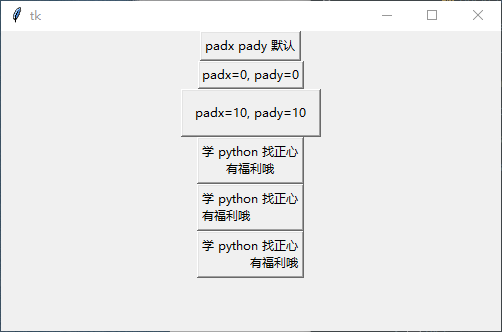
鼠标样式
python
# pencil:笔型
# circle:圆形
# hand1:手型 1
# hand2:手型 2
cursor = "鼠标的属性值"1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
python
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("500x300+100+100")
# 笔型
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="笔型", cursor="pencil")
button1.pack()
# 圆形
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="圆形", cursor="circle")
button2.pack()
# 手型 1
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="手型 1", cursor="hand1")
button3.pack()
# 手型 2
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="手型 2", cursor="hand2")
button4.pack()
root.mainloop()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
演示效果
需要把鼠标放 Button 上自行查看,会有不同显示
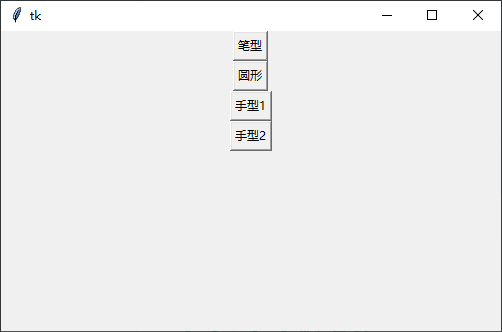
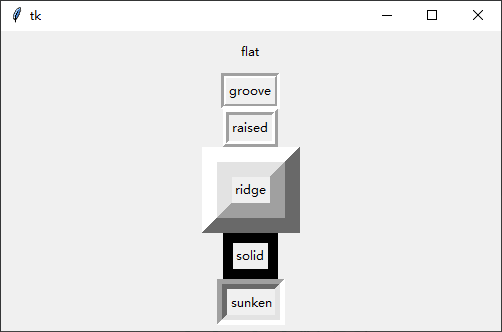
边框样式与宽度
python
# flat 无边框
# groove 中间凹
# ridge 中间凸
# raised 往中间凸
# solid 往中间凹
# sunken 不可以
relief = "边框样式值"1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
python
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("500x300+100+100")
# flat 无边框
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="flat", relief="flat", bd=8)
button1.pack()
# groove 中间凹
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="groove", relief="groove", bd=5)
button2.pack()
# ridge 中间凸
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="raised", relief="ridge", bd=6)
button3.pack()
# raised 往中间凸
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="ridge", relief="raised", bd=30)
button4.pack()
# solid 往中间凹
button5 = tk.Button(root, text="solid", relief="solid", bd=10)
button5.pack()
# sunken 不可以
button6 = tk.Button(root, text="sunken", relief="sunken", bd=10)
button6.pack()
root.mainloop()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
演示效果:
文字对齐方式
与 Label 一致
python
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("500x300+100+100")
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="e", width=10, height=3, anchor=tk.E)
button1.pack()
button2 = tk.Button(root, text="w", width=10, height=3, anchor=tk.W)
button2.pack()
button3 = tk.Button(root, text="s", width=10, height=3, anchor=tk.S)
button3.pack()
button4 = tk.Button(root, text="n", width=10, height=3, anchor=tk.N)
button4.pack()
root.mainloop()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
演示效果:
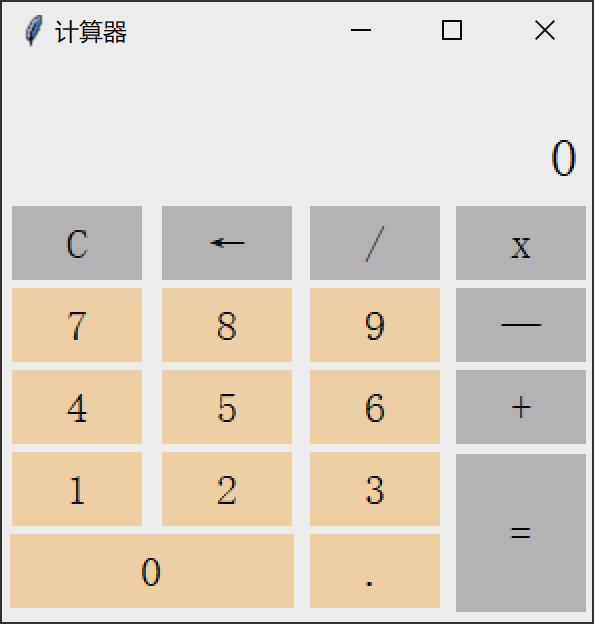
案例:计算器
制作一个简单的计算器程序要求所有功能按钮能正常使用,界面效果美观,效果如下:
代码:
python
# 导入模块,取别名
import tkinter as tk
# 实例化一个窗体对象
root = tk.Tk()
# 设置窗口的大小长宽为 300x300 出现的位置距离窗口左上角 +150+150
root.geometry("295x280+150+150")
root.title('计算器')
root.attributes("-alpha", 0.9)
root["background"] = "#ffffff"
lists = []
result_num = tk.StringVar()
result_num.set(0)
def num(i):
lists.append(i)
result_num.set(''.join(lists))
def operator(i):
if len(lists) > 0:
if lists[-1] in ['+', '-', '*', '/']:
lists[-1] = i
else:
lists.append(i)
result_num.set(''.join(lists))
def equal():
a = ''.join(lists)
end_num = eval(a)
result_num.set(end_num)
lists.clear()
lists.append(str(end_num))
def clear():
lists.clear()
result_num.set(0)
def back():
del lists[-1]
result_num.set(lists)
lable1 = tk.Label(root, textvariable=result_num, width=20, height=2, font=('宋体', 20), justify='left',
background='#ffffff', anchor='se')
lable1.grid(padx=4, pady=4, row=0, column=0, columnspan=4)
button_clear = tk.Button(root, text='C', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0',
command=lambda: clear())
button_clear.grid(padx=4, pady=4, row=1, column=0)
button_back = tk.Button(root, text='←', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0',
command=lambda: back())
button_back.grid(padx=4, row=1, column=1)
button_division = tk.Button(root, text='/', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0',
command=lambda: operator('/'))
button_division.grid(padx=4, row=1, column=2)
button_multiplication = tk.Button(root, text='x', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0',
command=lambda: operator('*'))
button_multiplication.grid(padx=4, row=1, column=3)
button_seven = tk.Button(root, text='7', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('7'))
button_seven.grid(padx=4, row=2, column=0)
button_eight = tk.Button(root, text='8', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('8'))
button_eight.grid(padx=4, row=2, column=1)
button_nine = tk.Button(root, text='9', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('9'))
button_nine.grid(padx=4, row=2, column=2)
button_subtraction = tk.Button(root, text='—', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0',
command=lambda: operator('-'))
button_subtraction.grid(padx=4, row=2, column=3)
button_four = tk.Button(root, text='4', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('4'))
button_four.grid(padx=4, pady=4, row=3, column=0)
button_five = tk.Button(root, text='5', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('5'))
button_five.grid(padx=4, row=3, column=1)
button_six = tk.Button(root, text='6', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('6'))
button_six.grid(padx=4, row=3, column=2)
button_addition = tk.Button(root, text='+', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0',
command=lambda: operator('+'))
button_addition.grid(padx=4, row=3, column=3)
button_one = tk.Button(root, text='1', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('1'))
button_one.grid(padx=4, row=4, column=0)
button_two = tk.Button(root, text='2', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('2'))
button_two.grid(padx=4, row=4, column=1)
button_three = tk.Button(root, text='3', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('3'))
button_three.grid(padx=4, row=4, column=2)
button_equal = tk.Button(root, text='=', width=5, height=3, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0',
command=lambda: equal())
button_equal.grid(padx=4, row=4, rowspan=5, column=3)
button_zero = tk.Button(root, text='0', width=12, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('0'))
button_zero.grid(padx=4, pady=4, row=5, column=0, columnspan=2)
button_decimal = tk.Button(root, text='.', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD',
command=lambda: num('.'))
button_decimal.grid(padx=4, row=5, column=2)
# 进入消息循环,显示窗口
root.mainloop()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111