DataFrame 基本操作
为了理解这些基本操作,将读取一个真实的股票数据。
提示
文件下载 stock_day.csv
python
import pandas as pd
# 读取文件
df = pd.read_csv("stock_day.csv")
# print(df)
# 删除一些列,让数据更简单些,再去做后面的操作
df = df.drop(["ma5", "ma10", "ma20", "v_ma5", "v_ma10", "v_ma20"], axis=1)
print(df.head())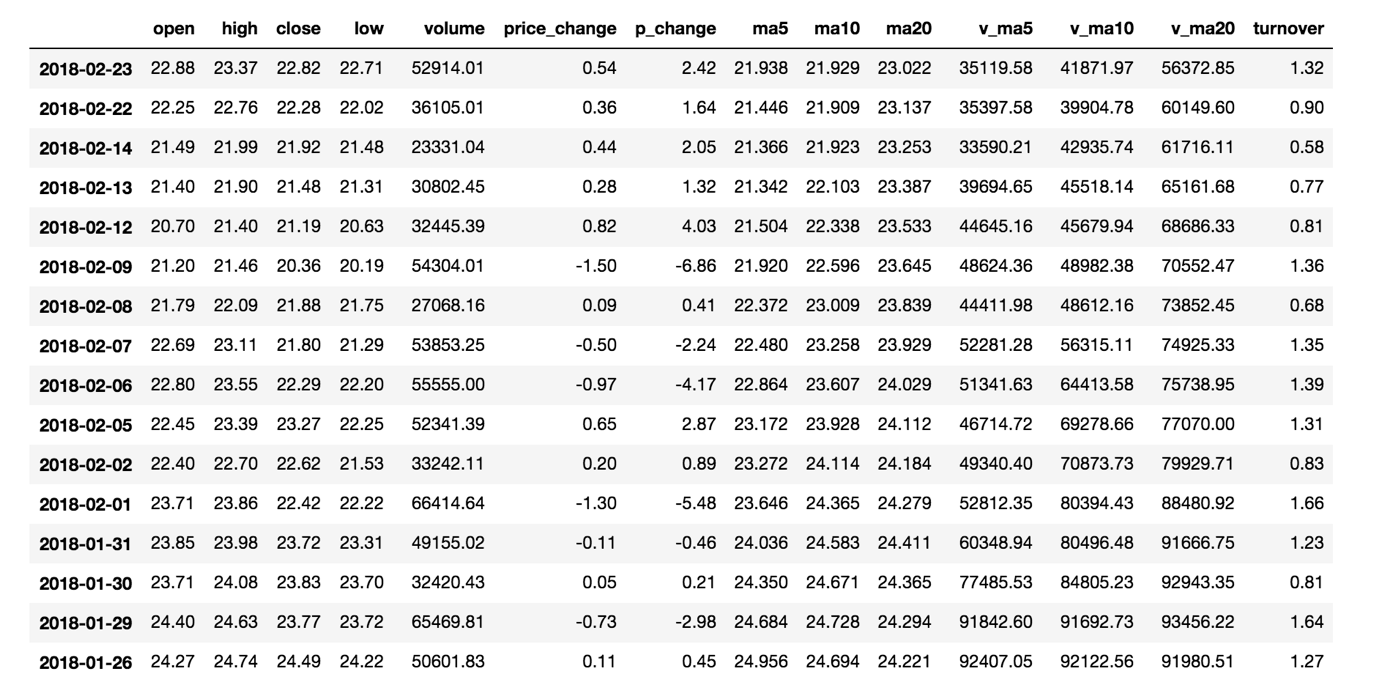
索引操作
Numpy 当中我们已经讲过使用索引选取序列和切片选择,pandas 也支持类似的操作,也可以直接使用列名、行名称,甚至组合使用。
直接使用行列索引 (先列后行)
获取 '2018-02-27' 这天的 'close' 的结果
python
# 直接使用行列索引名字的方式(先列后行)
print(df['open']['2018-02-27'])
"""
不支持的操作
print(data['2018-02-27']['open'])
print(data[:1, :2])
"""结合 loc 或者 iloc 使用索引
获取从 '2018-02-27':'2018-02-22','open' 的结果
python
# 使用 loc 只能指定行列索引的名字
print(df.loc['2018-02-27':'2018-02-22', 'open'])
2018-02-27 23.53
2018-02-26 22.80
2018-02-23 22.88
Name: open, dtype: float64
# 使用 iloc 可以通过索引的下标去获取
# 获取前 3 天数据,前 5 列的结果
print(df.iloc[:3, :5])
open high close low
2018-02-27 23.53 25.88 24.16 23.53
2018-02-26 22.80 23.78 23.53 22.80
2018-02-23 22.88 23.37 22.82 22.71使用 ix 组合索引
Warning:Starting in 0.20.0, the
.ixindexer is deprecated, in favor of the more strict.ilocand.locindexers.
获取行第 1 天到第 4 天,['open', 'close', 'high', 'low'] 这个四个指标的结果
python
# 获取行第 1 天到第 4 天,['open', 'close', 'high', 'low'] 这个四个指标的结果
# 使用 ix 进行下表和名称组合做引
print(df.ix[0:4, ['open', 'close', 'high', 'low']])
# 推荐使用 loc 和 iloc 来获取的方式
print(df.loc[df.index[0:4], ['open', 'close', 'high', 'low']])
print(df.iloc[0:4, df.columns.get_indexer(['open', 'close', 'high', 'low'])])
# 结果
open close high low
2018-02-27 23.53 24.16 25.88 23.53
2018-02-26 22.80 23.53 23.78 22.80
2018-02-23 22.88 22.82 23.37 22.71
2018-02-22 22.25 22.28 22.76 22.02赋值操作
对 DataFrame 当中的 close 列进行重新赋值为 1
python
# 直接修改原来的值
df['close'] = 1
# 或者
df.close = 1
print(df.close)排序
排序有两种形式,一种对于索引进行排序,一种对于内容进行排序
DataFrame 排序
- 使用
df.sort_values(by=, ascending=)- 单个键或者多个键进行排序,
- 参数:
- by:指定排序参考的键
- ascending:默认升序
- ascending=False:降序
- ascending=True:升序
python
# 按照开盘价大小进行排序 , 使用 ascending 指定按照大小排序
print(df.sort_values(by="open", ascending=True).head())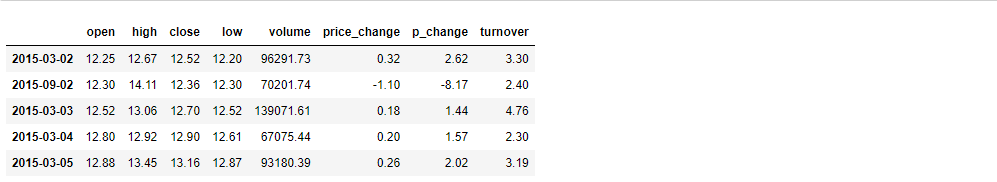
python
# 按照多个键进行排序
print(df.sort_values(by=['open', 'high']).head())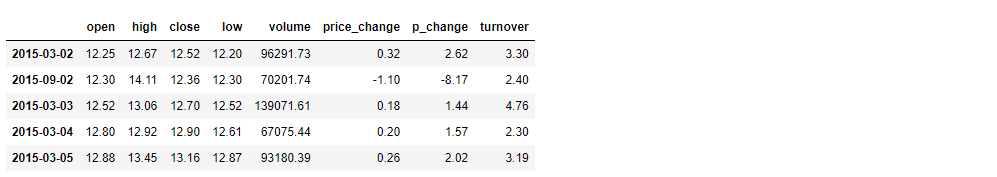
- 使用 df.sort_index 给索引进行排序
这个股票的日期索引原来是从大到小,现在重新排序,从小到大
# 对索引进行排序
df.sort_index()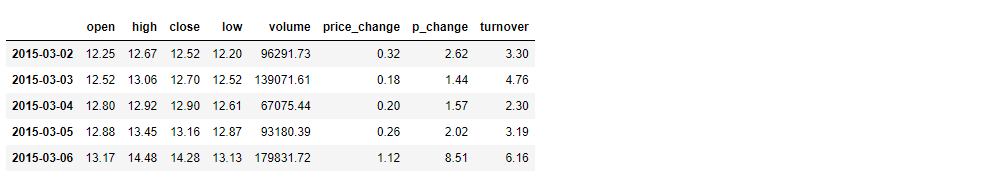
Series 排序
- 使用 series.sort_values(ascending=True) 进行排序
series 排序时,只有一列,不需要参数
python
print(df['p_change'].sort_values(ascending=True).head())
2015-09-01 -10.03
2015-09-14 -10.02
2016-01-11 -10.02
2015-07-15 -10.02
2015-08-26 -10.01
Name: p_change, dtype: float64- 使用 series.sort_index() 进行排序
python
# 对索引进行排序
print(df['p_change'].sort_index().head())
2015-03-02 2.62
2015-03-03 1.44
2015-03-04 1.57
2015-03-05 2.02
2015-03-06 8.51
Name: p_change, dtype: float64总结
- 索引【掌握】
- 直接索引 -- 先列后行,是需要通过索引的字符串进行获取
- loc -- 先行后列,是需要通过索引的字符串进行获取
- iloc -- 先行后列,是通过下标进行索引
- ix -- 先行后列,可以用上面两种方法混合进行索引
- 赋值【知道】
data[""] =data. =
- 排序【知道】
- dataframe
- 对象 .sort_values()
- 对象 .sort_index()
- series
- 对象 .sort_values()
- 对象 .sort_index()