案例:泰坦尼克号乘客生存预测
案例背景
泰坦尼克号沉没是历史上最臭名昭着的沉船之一。1912 年 4 月 15 日,在她的处女航中,泰坦尼克号在与冰山相撞后沉没,在 2224 名乘客和机组人员中造成 1502 人死亡。这场耸人听闻的悲剧震惊了国际社会,并为船舶制定了更好的安全规定。造成海难失事的原因之一是乘客和机组人员没有足够的救生艇。尽管幸存下沉有一些运气因素,但有些人比其他人更容易生存,例如妇女,儿童和上流社会。在这个案例中,我们要求您完成对哪些人可能存活的分析。特别是,我们要求您运用机器学习工具来预测哪些乘客幸免于悲剧。
我们提取到的数据集中的特征包括票的类别,是否存活,乘坐班次,年龄,登陆 home.dest,房间,船和性别等。
数据:http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/wiki/pub/Main/DataSets/titanic.txt

经过观察数据得到:
- 1 乘坐班是指乘客班(1,2,3),是社会经济阶层的代表。
- 2 其中 age 数据存在缺失。
步骤分析
- 1.获取数据
- 2.数据基本处理
- 2.1 确定特征值,目标值
- 2.2 缺失值处理
- 2.3 数据集划分
- 3.特征工程 (字典特征抽取)
- 4.机器学习 (决策树)
- 5.模型评估
代码实现
决策树算法 API
class sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(
criterion='gini', max_depth=None, random_state=None
)- criterion
- 特征选择标准
- "gini"或者"entropy",前者代表基尼系数,后者代表信息增益。一默认"gini",即 CART 算法。
- min_samples_split
- 内部节点再划分所需最小样本数
- 这个值限制了子树继续划分的条件,如果某节点的样本数少于 min_samples_split,则不会继续再尝试选择最优特征来进行划分。默认是 2.如果样本量不大,不需要管这个值。如果样本量数量级非常大,则推荐增大这个值。我之前的一个项目例子,有大概 10 万样本,建立决策树时,我选择了 min_samples_split=10。可以作为参考。
- min_samples_leaf
- 叶子节点最少样本数
- 这个值限制了叶子节点最少的样本数,如果某叶子节点数目小于样本数,则会和兄弟节点一起被剪枝。默认是 1,可以输入最少的样本数的整数,或者最少样本数占样本总数的百分比。如果样本量不大,不需要管这个值。如果样本量数量级非常大,则推荐增大这个值。之前的 10 万样本项目使用 min_samples_leaf 的值为 5,仅供参考。
- max_depth
- 决策树最大深度
- random_state
- 随机数种子
功能实现
导入需要的模块
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier1、获取数据
# 1、获取数据
titanic = pd.read_csv("titanic.csv")
print(titanic)
print(titanic.describe())2、数据基本处理
- 2.1 确定特征值,目标值
# 2.1 确定特征值,目标值
x = titanic[["pclass", "age", "sex"]]
y = titanic["survived"]- 2.2 缺失值处理
# 2.2 缺失值处理
# 缺失值需要处理,将特征当中有类别的这些特征进行字典特征抽取
x['age'].fillna(x['age'].mean(), inplace=True)- 2.3 数据集划分
# 2.3 数据集划分
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, random_state=22)3、特征工程 (字典特征抽取)
特征中出现类别符号,需要进行 one-hot 编码处理 (DictVectorizer),x.to_dict(orient="records") 需要将数组特征转换成字典数据
# 3.特征工程 (字典特征抽取)
# 对于 x 转换成字典数据 x.to_dict(orient="records")
# [{"pclass": "1st", "age": 29.00, "sex": "female"}, {}]
# print(x_train.to_dict(orient="records"))
transfer = DictVectorizer(sparse=False)
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train.to_dict(orient="records"))
x_test = transfer.fit_transform(x_test.to_dict(orient="records"))4、决策树模型训练和模型评估
决策树 API 当中,如果没有指定 max_depth 那么会根据信息熵的条件直到最终结束。这里我们可以指定树的深度来进行限制树的大小
# 4.机器学习 (决策树)
# estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy")
estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy", max_depth=5)
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 5.模型评估
print('预测结果', estimator.predict(x_test))
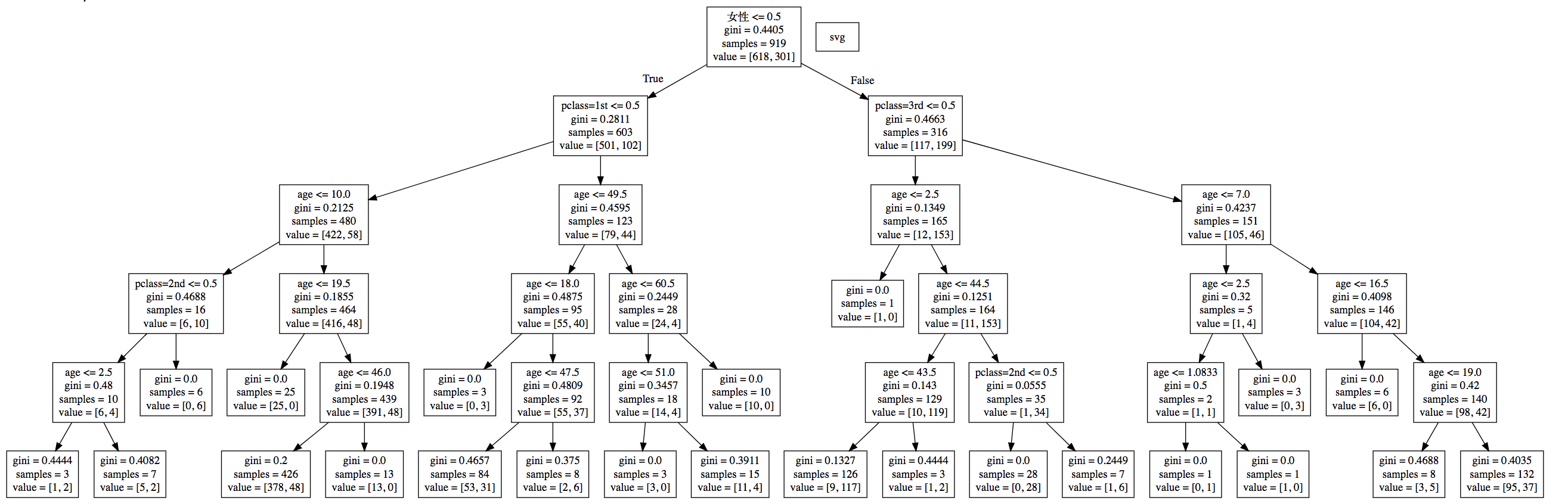
print('准确率:\t', estimator.score(x_test, y_test))决策树的结构是可以直接显示
决策树可视化
导出 dot 文件
sklearn.tree.export_graphviz() 该函数能够导出 DOT 格式
tree.export_graphviz(estimator,out_file='tree.dot',feature_names=['',''])
export_graphviz(estimator, out_file="tree.dot")dot 文件当中的内容如下
digraph
Tree
{
node[shape = box];
0[label = "petal length (cm) <= 2.45\nentropy = 1.584\nsamples = 112\nvalue = [39, 37, 36]"];
1[label = "entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 39\nvalue = [39, 0, 0]"];
0 -> 1[labeldistance = 2.5, labelangle = 45, headlabel = "True"];
2[label = "petal width (cm) <= 1.75\nentropy = 1.0\nsamples = 73\nvalue = [0, 37, 36]"];
0 -> 2[labeldistance = 2.5, labelangle = -45, headlabel = "False"];
3[label = "petal length (cm) <= 5.05\nentropy = 0.391\nsamples = 39\nvalue = [0, 36, 3]"];
2 -> 3;
4[label = "sepal length (cm) <= 4.95\nentropy = 0.183\nsamples = 36\nvalue = [0, 35, 1]"];
3 -> 4;
5[label = "petal length (cm) <= 3.9\nentropy = 1.0\nsamples = 2\nvalue = [0, 1, 1]"];
4 -> 5;
6[label = "entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 1\nvalue = [0, 1, 0]"];
5 -> 6;
7[label = "entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 1\nvalue = [0, 0, 1]"];
5 -> 7;
8[label = "entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 34\nvalue = [0, 34, 0]"];
4 -> 8;
9[label = "petal width (cm) <= 1.55\nentropy = 0.918\nsamples = 3\nvalue = [0, 1, 2]"];
3 -> 9;
10[label = "entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 2\nvalue = [0, 0, 2]"];
9 -> 10;
11[label = "entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 1\nvalue = [0, 1, 0]"];
9 -> 11;
12[label = "petal length (cm) <= 4.85\nentropy = 0.191\nsamples = 34\nvalue = [0, 1, 33]"];
2 -> 12;
13[label = "entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 1\nvalue = [0, 1, 0]"];
12 -> 13;
14[label = "entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 33\nvalue = [0, 0, 33]"];
12 -> 14;
}那么这个结构不能看清结构,所以可以在一个网站上显示
网站显示结构
将 dot 文件内容复制到该网站当中显示